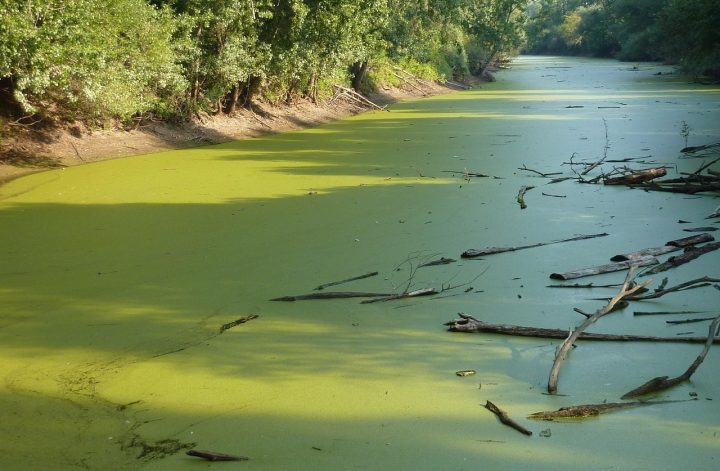
Dead Zones:
In the world’s oceans, there are regions or areas of water which have extremely low concentrations of oxygen- Hypoxia. These are called Dead zones.
In these dead zones the oxygen level falls as low as 2mg per liter of water which makes it extremely difficult for any flora or fauna to thrive or grow. Since many plants and animals are unable to live without sufficient oxygen levels these underwater regions become dead.
The lower the oxygen concentration drops the more dead and incapable of maintaining any aquatic life it becomes. They are approximately 405 dead zones in the world right now.
What Causes Dead Zone Formation?
Dead zones may be formed mainly due to oxygen depletion. They can be caused by both natural and man-made reasons.
Natural Causes of Dead Zone Formation:
Coastal upswells, wind direction or changes in wind patterns for long periods of time, water circulation patterns, other environmental factors like long term residency patterns, sunlight duration etc.
Moreover, enclosed bodies of water with not much movement also leads to the creation of dead zones. Climate change is also responsible for the oxygen reduction in the oceans and influences other factors as well.
Man-made Causes of Dead Zone Formation:
This is mainly caused by Eutrophication.
* Eutrophication: when chemical fertilizers are used on crops, the excess may runoff from the surface with rainfall and end up in lakes and streams which ultimately pour into the seas and wider oceans. This accumulation of nutrients like ammonium, nitrogen and phosphorus serves as food for the algae in the water.
As a result, they feed, expand and thrive in the water covering the surface. Certain kinds of algae like algae diatoms, cyanobacteria and the like thrive due to the availability of these nutrients. But this is not good for the rest of the aquatic life.
You Might Lile To Read: Eutrophication – Causes, Effects, and Solutions
What Are Phytoplankton And How They Benefit Our Environment?
This is because while other algae are usually consumed by fish and other species, cyanobacteria are not good food for most and hence they increase in population, thrive, cover the surface of the oceans which further hinders the photosynthetic ability of aquatic flora and fauna. When thee cyanobacteria, after accumulation die, they decompose. This decomposition utilizes the oxygen in the water that leads to hypoxic conditions causing the creation of dead zones.
Types of Dead Zones:
Dead Zones are of four types and categorized by the length of their duration. Those are:
- Seasonal Dead Zones: As indicated by its name, these types of dead zones occur seasonally, every year in mostly summer and autumn months of June-August and September-October. These are the most common types of dead zones that form in oceans due to monsoon season run off when rains have washed more fertilizers into the oceans.
- Permanent Dead Zones: These dead zones are permanent and form in deep waters. The oxygen concentration in deep water rarely exceeds 2mg/liter and hence this is why these areas are dead zones where aquatic life either evolve to live with minimum oxygen or not at all.
- Temporary Dead Zones: these are short lived dead zones where oxygen concentration may increase or decrease invariably. It may last for hours or days.
- Diel Cycling Hypoxia: This type of hypoxia is one in which the water becomes hypoxic only at night and in the early hours of the morning, typically during warmer temperatures. In areas with lots of flora but shallow water, this condition and occurrence is quite common.
Impacts of Dead Zones:
Although they may be created naturally, sometimes they are anthropogenic and may cause a number of impacts:
- Reduction of Biodiversity
- Eutrophication
- Toxic Algal blooms that release harmful toxins that can contaminate nearby drinking water and sources.
- Various illnesses for humans and animals due to poor water quality
- mass mortality of aquatic life due to depleted oxygen in water.
- Impacting the fishing community that have to travel farther from waters to catch fish.
Conclusion:
Dead zones by reducing the amount of oxygen available for flora and fauna underwater, can cause significant damage. However, for the most part the creation of dead zones is mostly caused by human activities than by natural reasons. It is yet another reason to adjust our lifestyles and switch to a more sustainable lifestyles in order to work against climate change that will further aggravate this phenomenon.
The largest Dead zone was found in the Gulf of Mexico and its creation is linked to the agricultural and meat industry practices in the surrounding zones. Around the world, dead zones have developed in continental seas, such as the Baltic sea, Black Sea, and the eastern Chinese sea, all of which are major fishery areas.
Check out, Impacts of Climate Change on Water Resources of Pakistan
and Anthropogenic Factors That Cause Species Decline
We hope you all liked this post! Please, comment below if you have any suggestions, comments, or feedback! We #envpk love hearing from our readers! Thanks!