Introduction
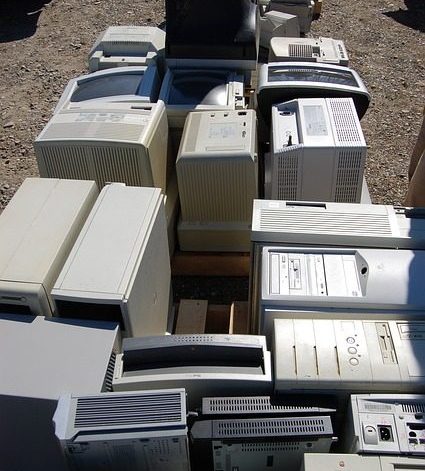
E-waste is the term given to waste that is generated from electronics. It is the discarded waste of used digital devices or electrical items that can no longer serve technical functions. The current era is revolving around information technology-based systems and items. It’s almost impossible to go out anywhere without a cell phone. Currently, there are almost 52 million metric tons of e-waste being generated globally. The annual e-waste production rate is increasing up to 5%. The e-waste generation would be doubled in the near future, as the world is growing faster in the development of new technologies.
Also check out: Electric Cars- Eco Friendly or Not?
Sources of E-waste
Sources of e-waste include: washing machines, refrigerators, dryers, irons, vacuum cleaners, fryers blenders, personal computers, laptops, cell phones telephones, instruments related to music, video and audio devices, fluorescent tubes, incandescent light bulbs, gas-discharge lamp, saws, drills, gardening machines, electrical toys, sports machines, models almost all electrical devices, thermostats, detectors, laboratory instruments coin-operated machines.
Also check out: 15 Environmental Problems Our World is Facing Right now

Impacts of E-waste on the Environment
E-waste has negative environmental impacts on all ecosystems. The absence of regulation to handle and dispose of e-waste is playing a critical role in increasing environmental pollution.
Air
E-waste is ignited in order to get metals that include gold, copper, steel, and aluminum. Toxic gases are released as a result of burning parts of electrical or digital devices.
Water
E-waste contains heavy metals that are very toxic to human health. The rains carry heavy metals and toxic compounds to water resources such as underground water and surface water causing water pollution.
Soil
The incineration of e-waste adversely affects the properties of soil. The leachate from disposed e-waste may cause water and soil pollution.
Ecosystem
The air, water, and soil pollution ultimately affect the whole ecosystem resulting in dangerous human and animal health impacts. The plants store heavy metals that are fed by animals and eventually make their way to humans. The health problems related to heavy metal consumption in terms of food and drinking water are severe.
Also check out: Improper Management of Solid Waste in Pakistan and Its Effects
Condition of E-waste in Pakistan
The condition of e-waste in Pakistan needs attention on a large scale. Pakistan is included in those third world countries where e-waste from other countries is imported for livelihoods.
OECD nations are responsible for almost 95 % of toxic waste and the exporting countries are Australia, United States, Germany, United Kingdom, and the Netherlands.
It would be more appropriate to say Pakistan- a dumping ground for international e-waste. The availability and selling of digital and electrical parts at fewer prices have made the import of e-waste quite easy. The imported e-waste is manually recycled, useful parts are segregated and the leftovers are dumped without proper disposal.
Pakistan is a member of some international conventions following as
– Basel Convention has a motto for transboundary movements of toxic wastes and their accurate disposal.
– Rotterdam Convention that works on banned pesticides and toxic chemicals
– Stockholm Convention includes the theme of Persistent Organic Pollutants
– Vienna Convention for the ozone layer protection
– Montreal Protocol on chemicals that destroy the ozone layer
The actual problem is the implementation of these regulations. Environmental Protection Act of 1997, has put a ban on open dumping but Liyari and Surjani of Karachi can clearly be observed as open dumping sites for e-waste. All age groups are found working there for livelihoods.
Also check out: Cryptocurrency Mining and Its Negative Impact on Environment

Possible Solutions
Public awareness regarding e-waste handling and disposal is a must. People should be made aware of the health impacts linked with e-waste. An expert technical team along with the availability of adequate financial resources should be prepared by the Government who has working experience e of handling and managing e-waste. The Government should work on the implementing strategies of the Basel Convention. There should be an allotment of funds for developing countries by the developed countries to raise awareness among different age groups who work in such fields.
Conclusion
Third-world countries of the world are used as dumping ground for international e-waste. Pakistan is also included in those countries. In Pakistan disposal plans and sites are required for the management of e-waste. There is already a lack of surveillance regarding municipal solid waste management; during such circumstances, e-waste is increasing environmental problems.
Recommendations
The government of Pakistan should take action against the mafia that is involved in the import of e-waste. The country needs more laws and tactics against e-waste management.
You might also wish to read: Environmental Impact of Ship Breaking Industry in Pakistan
I hope you all liked this post! Please comment below if you have any suggestions, comments, or feedback! We at #envpk love hearing from our readers! Thanks!




2 Comments
I recently went through this website and I’m simply impressed by the way you all have collected this much data related to the environment. Thank you so much as this is really helpful.
We are glad you were impressed by our website and content. And you are welcome Muzamil!